URL Slug for SEO: What it is and best practices
What is a URL Slug?
A URL slug is the part of the URL that references a unique page on a website.
URL slugs should be easy-to-read, because they play an important role in describing what is on a page to both search engines and visitors. Think of it like a name-tag used to identify each page on a website.
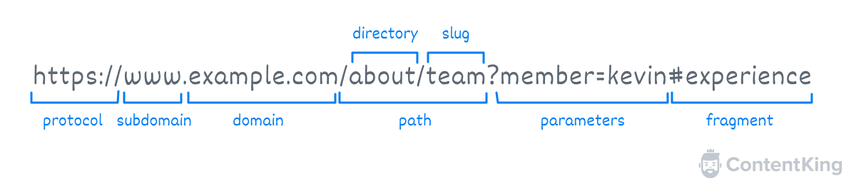
URL slugs will come after the directory, and before any additional parameters/fragments. It is the part of the URL that changes for each unique page, whereas other parts of the URL, like the protocol and domain name, stay the same.
The URL slug is sometimes referred to as a “website slug'' or “page slug”, but for the sake of simplicity we will refer to it as a “URL slug”.
URL slug vs. URL Path: what’s the difference?
People often refer to “URL path” when talking about URL slugs.
The URL path, as the name suggests, provides a map to the exact location of a certain page. This includes the directory and URL slug — however parameters and fragments are not part of the path as these parts do not take you to a new page, but rather modify content on an existing page and take you to a specific section of the page.
To help make this clear, let’s take an example to zoom in on this:
- URL:
https://www.conductor.com/academy/urls/ - Path:
/academy/urls/ - Slug:
urls
The path may include subdirectories if these are used, but will always include the slug. It can also include a file extension, such as .html or .php.
Why is a URL slug important for SEO?
URL slugs are important to search engines because they are important to visitors.
While the URL slug itself won’t have a direct impact on your rankings, it will influence the visitor’s decision making process for whether or not to click on your site. URL slugs are part of the snippet shown in the SERP, and are an indicator to visitors if the page will have related content and satisfy what they are searching for.
It also contributes to overall user experience — messy URLs can be confusing and unclear to visitors and even lead to them questioning the quality of your site.
URL Slugs Best Practices
Now let’s get into the best practices for how to write URL slugs.
- Make them readable
- Include relevant keywords
- Keep it short
- Future-proof by removing dates and numbers
- Stick to lower-case
- Use hyphens
Make them readable
URL slugs should make it clear what’s on the page right away, so it’s important that they are easy to read and understand. This means keeping it short, to the point, and without any unnecessary characters like numbers or symbols.
For example, a URL slug like contact leaves no question that this is the page to go to for contact information. Not only is this easy to read, it also has the added benefit of being easy to remember so visitors can conveniently come back to it at a later time.
Include relevant keywords
Because it’s an indicator of what’s on the page, URL slugs should contain relevant keywords. Don’t get carried away though — focus on using a keyword (or keywords) that accurately describe the page’s content and matches the searcher’s intent.
Keep it short
There is no such thing as a perfect slug length.There’s no exact number of characters you should use, but there are some guidelines to follow.
Generally, the shorter the better. Google prefers shorter URLs and if two pages have identical metrics, the shorter one will rank higher with URL length being the tie-breaking parameter.
Shorter URLS make it easier for both search engines and visitors to understand the page, and it looks more attractive in SERPs. For example, which URL do you think visitors are more likely to click on:
https://example.com/pricing/
or
https://example.com?pageId=2b5ebr965f41cbb6f949f740g1
Keep in mind that URL slugs should still be descriptive. It shouldn’t be so short that the searcher can’t make out what the page is about, but it also doesn’t need to be the entire length of the title. As we said before, focus on select keywords that reflect the page’s content.
Another way to shorten the slug without compromising context is by removing any unnecessary stop-words like a, and, or the. This also helps with readability.
Future-proof by removing dates and numbers
Including numbers and dates in URL slugs makes it difficult to reuse the page later on if you want to update content.
For example, using a slug like /10-SEO-tips-in-2016/ limits the page’s content to those set parameters. Say you want to add more SEO tips so you end up with 23 SEO tips or if you want to make it more timely, like SEO tips for 2022, you’ll either have to use a redirect to a newer version of the page or let the content appear outdated. Either way, it’s not an ideal situation so it’s best to avoid numbers and dates.
Stick to lower-case
Since everything after the domain can be case-sensitive, using only lower-case URL slugs is common practice to avoid duplicate content issues and 404 errors. You want to minimize the risks of folks creating incorrect links to your pages, and you want to make it as easy as possible for visitors to adjust URLs in their browser’s address bar.
Use hyphens
Use hyphens (-) to separate words so that URL slugs are clean and readable. While you should limit the use of other characters and symbols, hyphens are an exception and have become common practice in this particular use-case. It’s also Google’s recommended punctuation.
How to change your URL slug in WordPress
If you are using WordPress, you are likely familiar with the term permalink. But what is a permalink exactly?
A permalink is the full URL for content published on WordPress. This includes the protocol, subdomain, domain and slug. The idea is that this link is permanent and shouldn’t change overtime (permanent + link = permalink).
WordPress sets a default URL structure, but also provides options to create custom URL structures by adjusting your permalink settings .
Given the best practices we discussed above, we recommend changing URL slugs from the default URL slug WordPress typically creates itself, to one that is more SEO friendly.
🚨 Caution ahead
Changing permalink settings on a production website, and adjusting URL slugs for pages that already exist will dramatically impact its SEO performance, so proceed with caution. Ideally, you define the website’s permalink structure upfront, and not touch it.
If you do decide to make changes, be sure to update any internal links to the affected pages and implement redirects where needed. Redirects will help retain page authority and thereby minimizing the damage to rankings.
With that said, here's how you can change URL slugs for pages in WordPress:
Change your URL slug in WordPress
- Login into WordPress.
- Go to the Page with the URL you’d like to change. If this is a new page, you first need to save it as a Draft.
- Under the Title field, you’ll see a URL that was generated.
- Click the Edit button and type in the new slug.
- Save the new slug.
So keep in mind how you want your site’s URL structure to look and have set guidelines — this will keep your site’s URL consistent, making it easier for search engines to crawl and provide a better experience to visitors.



